The Importance of Urgent Care for Falls and Shoulder and Elbow Injuries
December 17, 2024
Elbow Fractures and Dislocations – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
December 17, 2024When to operate on a rotator cuff tear?
A shoulder surgery specialist’s perspective
Rotator cuff injuries are common and can cause significant shoulder pain and disability. But when is the right time to consider surgery? In this article, we’ll explore the various aspects of rotator cuff tears, from their definition to the details of surgery and recovery.
1. What is the rotator cuff?
The rotator cuff is a group of tendons and muscles that surround and stabilize the shoulder joint. This structure is crucial in aiding movement and providing stability to the shoulder during work, sports, and everyday activities.
2. What are the types of rotator cuff tears and how can they happen?
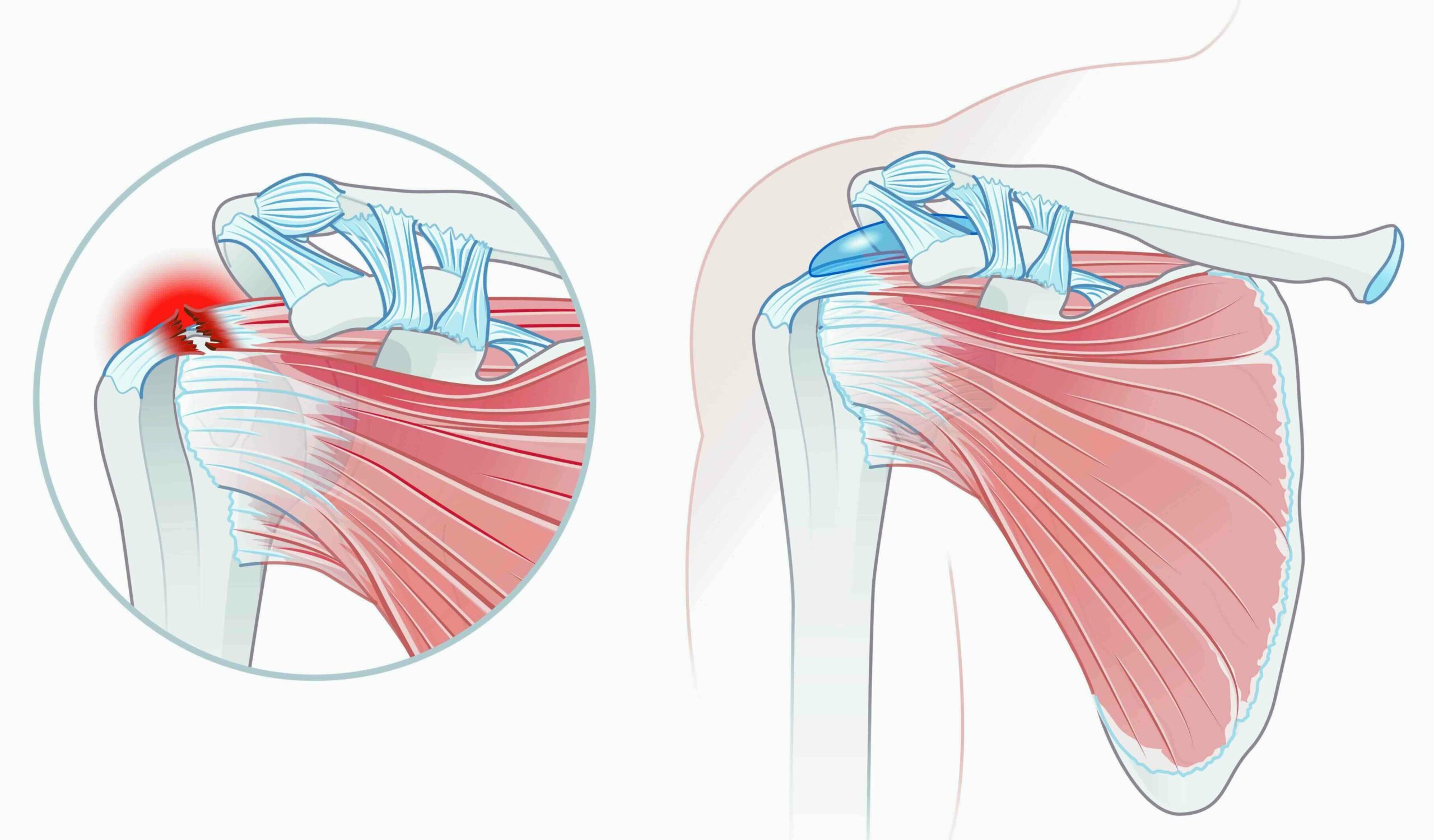
Rotator cuff tears can vary in terms of the mechanism of injury, severity, and extent. They can occur due to acute injuries such as a fall, direct trauma, or excessive loads borne by the shoulder. However, the most common cause is progressive wear and tear over time, especially in people involved in repetitive activities that require overhead movement of the arm.
The extent of the tear can be categorized as partial or complete tears, if it involves the entire thickness of the tendon insertion region. They can also be classified according to the number of tendons involved and their size. Although it may be counterintuitive, more extensive tears do not necessarily translate into more severe symptoms. It is believed that the adaptability of the remaining muscles around the shoulder may allow for near-normal function, provided there is time for it to do so, as is the case with tears that develop very slowly over time.
3. What are the main symptoms of rotator cuff tears?
Symptoms of rotator cuff tears can vary from person to person, but they usually include shoulder pain, especially during activities that involve lifting the arm overhead, weakness, and decreased range of motion. The pain may be worse at night, especially when lying on the affected shoulder.
4. What is the timing for rotator cuff repair surgery?
The decision to perform rotator cuff repair surgery depends on several factors, including the severity of the injury, the patient’s age and activity level, and the effectiveness of conservative treatment. In general, surgery is considered urgent for patients of working age with full-thickness tears and those caused by trauma. In these cases, tendon repair should be performed as soon as possible to prevent tendon retraction and muscle atrophy. These are factors that increase the likelihood of successful surgery and recovery to pre-injury levels.
In the case of chronic or degenerative tears, surgery should be considered when symptoms persist despite non-surgical treatments, such as physiotherapy. A well-guided rehabilitation program by a multidisciplinary team, including a physiatrist and physiotherapist, among other professionals, can ensure an excellent recovery and avoid the need for surgery. However, when complaints persist after 3 to 6 months of adequate conservative treatment, surgical repair can help restore the function of the rotator cuff tendons and improve shoulder activity.
5. What does rotator cuff repair involve?
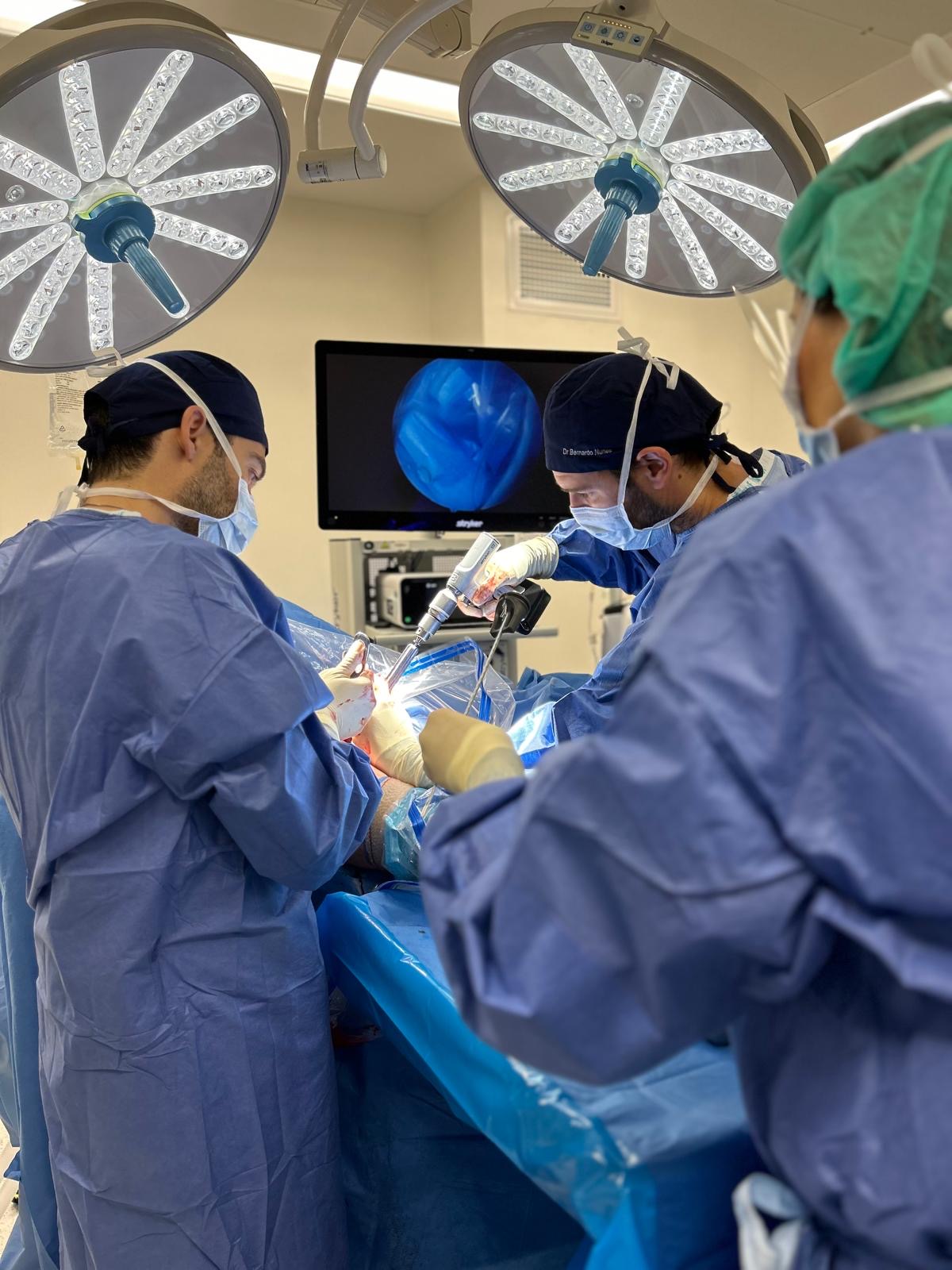
Rotator cuff repair surgery is performed to suture or reconstruct the damaged tendons, thereby restoring function and stability to the shoulder. The procedure is currently performed entirely by arthroscopy, a minimally invasive video-assisted surgery technique that involves small incisions and the use of a viewing device called an arthroscope. This technique has advantages in improving the visualization of the affected structures, the ability to repair, and a shorter recovery time.
During surgery, damaged tendons are identified, prepared, and then reattached to their origin in the bone, usually using small suture-supported implants called anchors. In some cases, additional procedures may be needed, such as releasing scar tissue or repairing other structures in the shoulder.
6. What to expect from recovery after rotator cuff repair surgery?
Recovery after rotator cuff repair surgery can vary from person to person, but it usually involves a period of temporary immobilization of the shoulder, followed by a progressive rehabilitation program. Patients can expect to see a gradual improvement in shoulder pain and function over time, but the recovery process may take several months before maximum benefit is achieved.
During rehabilitation, patients work with physiatrists and physical therapists to strengthen shoulder muscles, restore range of motion, and improve joint stability. It is important to follow the instructions of your doctors and physical therapists to ensure a full recovery and avoid complications.
The decision to operate on rotator cuff tears should be carefully considered based on an individual patient assessment and treatment goals. If you are experiencing symptoms of a rotator cuff injury, consult an orthopaedic shoulder specialist for a thorough evaluation and discussion of available treatment options.